[0] day4복습
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : day04 복습
*/
package Java0327;
public class _00_review {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 반복문
// for문
/*
초기식 한번만 작성!
계속 반복은 2, 3, 4번 실행
for( ①초기식 ; ②조건식 ; ④증감식 ) {
③반복될 실행문
]
⑤ 종료
*/
// // for문의 다른방법
// int i= 1;
// for( ; i<=10 ;) {
// System.out.println(i);
// i++;
// }
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) {
// sum(변수) = sum(값) +i;
// sum += i;
}
// continue : 이후 문장 실행하지 않고 증감식으로 이동(반복문 끝 x)
// break : break문이 실행되는 기점으로 반복문 종료
}
}//for문의 실행조건 잘 기억하고 공부하기!!
[1] whlie문
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : while문
*/
package Java0327;
public class _01_while {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
while(반복조건) {
반복할 실행문
}
*/
/*
초기식
while(조건식) {
실행문
증감식
}
1부터 10까지 더하는 반복문 작성!
*/
// for문과 while문의 차이점
// for문은 반복횟수를 정하고 반복문을 실행
// while문은 반복 횟수를 정하지 않고 반복문을 실행
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
while(i<=10) {
sum = sum + i;
i++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}//기본 while(반복조건) 기억하기!
[2] whlie문 예제(주사위 던지기)
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : while문 예제
*/
package Java0327;
public class _02_whileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 주사위를 던져서 5가 나오면 종료하는 프로그램 만들기
// 프로그램을 실행하는 변수
boolean run = true;
// 주사위 던진 횟수 구하는 변수
int cnt = 0;
// 주사위 값을 구하는 변수
int dice = 0;
while(run) {
// 주사위 던지기 Math.random()
dice = (int) (Math.random() * 6) +1;
// 카운트 증가
cnt++;
if (dice == 5) {
run = false;
}
// 주사위 값 출력
System.out.println("주사위 값 : " + dice);
}
System.out.println(); // 줄 띄어 쓰기
System.out.println("던진 횟수 : " + cnt);
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
// 정수형
// byte 0
// short 0
// int 0
// long 0L
// 실수형
// float 0.0f
// double 0.0
// 문자형
// char '\n0000'
// 논리형
// boolean false
// 그외에(참조형)
// String 등등 null
}
}//while문 안에서도 조건문 실행이 가능하다!
[3] whlie문 예제(ATM기 만들기)
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : bank1
*/
package Java0327;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _03_bank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 변수의 이름!! (영어로 하기)
int account = 0;
// while문 실행을 위한 조건변수 run을 true로 선언
boolean run = true;
// 메뉴 선택하기 위한 변수
int menu;
// 입력받기 위한 객체
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(run) {
System.out.println("=============================");
System.out.println("1.예금 | 2.출금 | 3.잔고 | 4.종료");
System.out.println("=============================");
System.out.print("선택 : ");
menu = sc.nextInt();
switch(menu) {
case 1:
System.out.println(" 입금액 : ");
// int a= sc.nextInt();
// account = account + a;
account += sc.nextInt();
break;
case 2:
System.out.print(" 출금액 : ");
int b = sc.nextInt();
// account = account - b;
// account -= sc.nextInt();
if(account >= b) {
account -= b;
} else {
System.out.println("잔액이" +(b-account)+"부족합니다.");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(" 잔고 : " + account +"원");
break;
case 4:
run = false;
System.out.println(" 이용해주셔서 감사합니다. ");
break;
default:
System.out.println(" 다시 입력해주세요! ");
break;
}
}
}
}//앞에서 본것 같이 조건문을 사용해서 결과값을 추출할 수 있다.
//출력값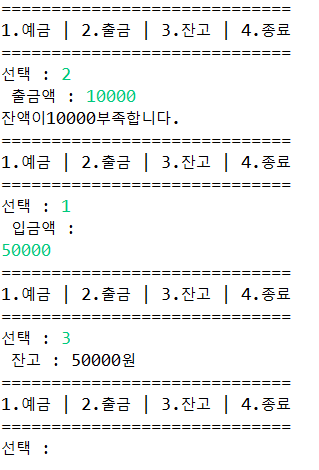
[4] whlie문
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : do-while문
*/
package Java0327;
public class _04_doWhile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// while문과 do-while문의 차이점
// [1] while문 : 반복문을 실행하기 전에 조건식 검사
// [2] do-while : 반복문을 실행한 후에 조건식 검사(무조건 한번은 실행)
/*
do {
반복될 실행문;
} while(반복조건);
*/
int i = 10;
// System.out.println("while문 실행!");
// while(i<10) {
// System.out.println("" +i);
// i++;
// }
do {
System.out.println("i : " +i);
i++;
} while(i<10);
}
}//출력
>>i : 10
[5] do-whlie문을 이용한 up&down 게임
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : do-while문을 이용한 up&down 게임
*/
package Java0327;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _05_upDown {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 입력받기 위해 Scanner 객체 생성
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 정답은 1~45사이의 랜덤한 숫자
int answer = (int)(Math.random() * 45) + 1;
int input = 0; //입력한 숫자
int count = 0; //입력한 횟수
// 프로그램 반복을 위한 변수
boolean run = true;
System.out.println("UP & Down 게임 시작!");
do {
System.out.println("1부터 45사이의 숫자를 입력 : ");
input = sc.nextInt(); //숫자 입력
count++; // 숫자를 입력할 경우 카운트 증가
if(answer > input) { // 입력한 값이 정답보다 클 경우
System.out.println("입력한 값이 정답보다 큽니다");
} else if(answer < input) { //입력한 값이 정답보다 작을 경우
System.out.println("입력한 값이 정답보다 작습니다");
} else { System.out.println("정답 : "+ answer+" 시도수 " + count
+"횟수"); //입력한 값이 정답일 경우
run = false;
}
//조건문을 달아서 더욱 어렵게 만들기
// if(count <=3) {
// System.out.println("통과");
// } else {
// System.out.println("벌칙");
// }
} while(run);
}
}//출력
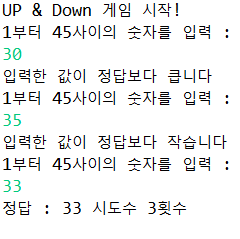
[6] array 배열 중요!!


Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 2 out of bounds for length 2
at Java0327._06_array.main(_06_array.java:38)왜 발생했는지? 배열을 지정할때 크기를 지정하고 구한다.
해결 방법은? 생각보자!
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : array 배열
*/
package Java0327;
public class _06_array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 배열(array) : 같은 (변수)타입의 데이터를 하나의 변수에 저장하는 구조
// int num1, int num2, int num3 => numbers
// 배열 선언
// (1) 타입[] 배열이름;
int[] nums;
// (2) 타입 배열이름[];
int numbers[];
// 변수의 선언과 할당
// int i;
// i = 10;
// int j = 20;
// 배열의 선언과 할당
int[] num; //선언
num = new int[] {10, 20}; //할당
int[] numArr = {1,2,3}; //선언과 할당 동시에 가능(주로씀)
// 배열 초기화
num = new int[] {10, 20};
// 배열값 출력
// System.out.println("첫번째 값 : " + num[0]);
// System.out.println("두번째 값 : " + num[1]);
int number[] = {10,20,30,40};
// Q. number 배열의 값을 출력하시오.
// System.out.println("첫번째 값 : " + number[0]);
// System.out.println("두번째 값 : " + number[1]);
// System.out.println("세번째 값 : " + number[2]);
// System.out.println("세번째 값 : " + number[3]);
//
// int numberLength = numArr.length;
//
// char[] chArr = {'인', '천', '일', '보'}; // 데이터 타입이 정해준데에서만 배열 가능!! 중요!!!
// String[] strArr = {"index0", "index1", "index2"};
//
// // 배열의 크기 : length(길이); 명령어를 사용해서 크기 알기
// int chLength = chArr.length;
// int strLength = strArr.length;
//
//
// System.out.println("chArr 배열의 크기 : " + chLength); //4
// System.out.println("strArr 배열의 크기 : " + strLength); //3
/*
for(int i=0; i<= 배열의크기(length) ; i++) {
반복문 실행
i가 0부터 시작, i는 배열의 크기보다 작다!!
}
Q. 반복문을 사용해서 number배열 출력하시오
*/
// for(int i=0; i<number.length; i++) {
// System.out.println("number[" + i +"] : " + number[i]);
// }
// Q.Java, DB, HTML 과목의 점수를 배열에 저장하고
// 세과목의 총점과 평균을 구하시오
// Java = 90점, DB = 80점, HTML = 84점
// int[] score <= 과목점수 입력
// int sum;
// double avg;
// score[0], score[1], score[2] 사용금지!
// 나누기 3도 금지
int[] score = {90, 80, 84};
int sum =0;
double avg=0;
for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) {
// 각 과목의 점수 출력
System.out.println("score[" + i +"] : " + score[i]);
// 세과목의 합
sum += score[i];
}
System.out.println("총점 : " + sum + "점");
//평균
avg = (double)sum / score.length;
System.out.println("평균 : " + avg +"점");
// 평균(소숫점 두자리까지 반올림) : 84.67
avg = (Math.round(avg*100) / 100.0);
// avg : 84.666666667
// avg * 100 : 8466.66666667
// Math.round(avg) : 8467 // Math.round이 함수는 반올림 함수!!
// 8467 / 100.0 : 84.67
System.out.println("평균(소숫점 두자리) : " + avg +"점");
}
}//출력

[7] array 배열 예제 중요!!
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : array 배열 예제
*/
package Java0327;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _07_arrExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 입력 Scanner
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
// 총점과 평균 변수
int sum = 0;
double avg = 0;
// 입력받을 과목 갯수 정하기(배열의 크기 정하기)
System.out.println("입력 받을 과목 갯수 : ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
// 갯수에 따른 배열 생성
int[] score = new int[n];
// 반복문을 활용해서 배열 입력
for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) {
//입력
System.out.println((i+1) + "번 과목 점수 입력 : ");
score[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) {
//출력
System.out.println((i+1) + "번 과목 점수 입력 : " + score[i]);
}
for(int i=0; i<score.length; i++) {
//합계
sum += score[i];
}
System.out.println("총점 : " + sum + "점");
//평균
avg = (double)sum / score.length;
avg = (Math.round(avg*100) / 100.0);
System.out.println("평균(소숫점 두자리) : " + avg +"점");
}
}//출력

[8] coin (생각해보기)!
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : coin
*/
package Java0327;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _08_coin {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Q. 동전 갯수를 구하는 예제
// 어떤 금액을 입력하면
// 각 동전이 몇개씩 필요한지 출력하는 문제
// ex) 2680원
// 500원 : 5개
// 100원 : 1개
// 50원 : 1개
// 10원 : 3개
// 규칙을 찾아서 배열을 사용해서 문제를 해결하시오
// 2680 - (500 x 5) = 180
// 180 - (100 x 1) = 80
// 80 - (50 x 1) = 30
// 30 - (10 x 3) = 0
int[] coin = {500, 100, 50, 10};
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("금액을 입력하시오 : ");
int money = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<coin.length; i++) {
int count = money / coin[i];
money = money % coin[i]; //money %= money % coin[i];
System.out.println(coin[i] + "원 동전 갯수 : " + count);
}
}
}//출력

[9] 배열 검색(특이점 파악하기)
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : 배열 검색
*/
package Java0327;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _09_arraySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 주어진 배열의 값이 어떤 index에 위치하는지 알아본느 예제
int[] num = {8, 2, 6, 1, 3, 4, 10, 7, 5, 9};
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
// System.out.println("1부터 10사이의 숫자 입력 : ");
// int value = sc.nextInt();
//
// int idx = 0;
//
// for(int i =0; i<num.length; i++) {
// if(value == num[i]) {
// idx = i+1;
// break;
// }
// }
// System.out.println("입력한 값 " + value + "는(은) " + idx + "번째 있다.");
char[] icia = {'인', '천', '일', '보', '아', '카', '데', '미'};
System.out.println("\"인천일보아카데미\" 중에서 한글자 입력 : ");
char value = sc.next().charAt(0);
int idx = 0;
for(int i =0; i<icia.length; i++) {
if(value == icia[i]) {
idx = i+1;
System.out.println("입력한 값"+"'"+value+"'는(은)"+idx+"번쨰 있다.");
break;
}
}
if(idx==0) {
System.out.println("해당하는 값이 없습니다!");
}
}
}//출력

[10] 배열 복사(특이점 파악하기)
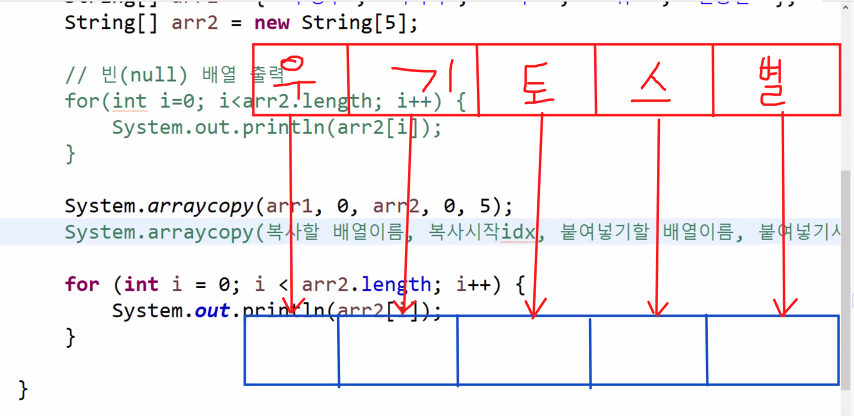
/**
* Date : 2023.03.27
Author : funling
Description : 배열 복사
*/
package Java0327;
public class _10_arrayCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 배열 복사
String[] arr1 = {"우영우", "기러기", "토마토", "스위스", "별똥별"};
String[] arr2 = new String[5];
// 빈(null) 배열 출력
// for(int i = 0; i<arr2.length; i++) {
// System.out.println(arr2[i]);
// }
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 2);
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 0, 5);
// System.arraycopy(복사할 배열이름, 복사시작idx, 붙여넣기할 배열이름, 붙여넣기시작idx, 복사할배열크기)
for(int i = 0; i<arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr2[i]);
}
}
}//출력

'IT코딩공부!' 카테고리의 다른 글
| #7 day6복습, 필드,생성자,메소드(main)공부 (0) | 2023.03.29 |
|---|---|
| #6 day5복습, array(1,2차원 배열 공부) (0) | 2023.03.28 |
| #4 day3복습, for문 공부 (0) | 2023.03.24 |
| #3. day2아침 복습, if(조건문)공부 (0) | 2023.03.23 |
| #2 오전 아침 복습 및 2일차 공부 일지(Int, Char, String, Boolean) (0) | 2023.03.22 |




