IT코딩공부!
#7 day6복습, 필드,생성자,메소드(main)공부
history.
2023. 3. 29. 17:34
혼자 공부하는 자바
혼자 해도 충분하다! 1:1 과외하듯 배우는 자바 프로그래밍 자습서 (JAVA 8 &11 지원) 이 책은 독학으로 자바를 배우는 입문자가 ‘꼭 필요한 내용을 제대로’ 학습할 수 있도록 구성했다. ‘무엇을’ ‘어떻게’ 학습해야 할지 조차 모르는 입문자의 막연한 마음을 살펴, 과외 선생님이 알려주듯 친절하게, 그러나 핵심적인 내용만 콕콕 집어준다. 책의 첫 페이지를 펼쳐서 마지막 페이지를 덮을 때까지, 혼자서도 충분히 자바를 배울 수 있다는 자신감과 확신이 계속될 것이다! 20명의 베타리더 검증으로, ‘함께 만든’ 입문자 맞춤형 도서 20명의 베타리더와 함께 구성하여 입문자에게 맞는 난이도, 분량, 학습 요소 등을 적극 반영했다. 어려운 용어와 개념은 한번 더 풀어 쓰고, 복잡한 설명은 눈에 잘 들어오는 그림으로 풀어 냈다. ‘혼자 공부해본’ 여러 입문자의 초심과 눈높이가 책 곳곳에 반영된 것이 이 책의 가장 큰 장점이다.
- 저자
- 신용권
- 출판
- 한빛미디어
- 출판일
- 2019.06.10
[0] day6복습

/**
* Date : 2023.03.29
Author : funling
Description : day6복습
*/
package Java0329;
public class _00_review {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 배열 : 같은 타입의 데이터를 하나의 변수에 저장하는 구조
// 차이점!!
// 1차원 배열
// 타입[] 배열이름 = new 타입[j];
// 2차원 배열
// 타입[][] 배열이름 = new 타입[i][j]
// i행 j열!! 기억
// 2차원배열 반복문
// i(행)에 배열의 크기
// array.length
// j(열)에 배열의 크기
// array[i].length
String[] stu = {
"김상훈", "김정태", "김하나", "마윤호",
"벡기호", "박현상", "성민규", "유혜순",
"윤현수", "이성종", "이예진", "임가희",
"조형섭", "한혜휘", "황인철", "박준수"
};
String[][] group = new String[4][4];
for(int i=0; i<group.length; i++) {
for(int j =0; j<group[i].length; ) {
int n = (int)(Math.random() * 16);
if(stu[n] != null) {
group[i][j] = stu[n];
stu[n] = null;
j++;
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<group.length; i++) {
System.out.println("===" + i + "조===");
for(int j =0; j<group[i].length; j++ ) {
System.out.println(group[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}// 팀 과제를 을 위해 랜덤 함수를 사용하고 거기의 2차원배열을 사용해서 팀 구성을 해보았다.
[1] 필드, 생성자, 메소드 (기본 구조) 알기!
(1) 필드
클래스의 3가지 요소
// [1] 필드
// - 명사형, 값의 상태 관리, 데이터를 저장...
String company; //제조회사
String color; //제품색상
int price; //제품가격
int size; //제품크기
int temp; //현재온도//필드의 명시되어 있는것 처럼 각 타입의 변수를 지정해 준다!
(2) 생성자
[2] 생성자
/*
생성자의 기본구조
_01_airCon(매개변수){
}
(1) 기본생성자
: 괄호안(매개변수)에 아무것도 없는 생성자
: java 컴파일러가 기본적으로 생성자가 없을 경우 자동으로 만들어준다.
: 단 매개변수 생성자를 생성했을 경우 따로 만들어줘야 사용할 수 있다.
*/
_01_airCon(){
}
// (2) 매개변수 생성자 : 괄호안(매개변수)에 필드를 선언한다.
_01_airCon(String company){
this.company = company;
}
_01_airCon(String company, String color){
this.company = company;
this.color = color;
}
_01_airCon(String company, int size){
this.company = company;
this.size=size;
}
_01_airCon(int price, String company){
this.company = company;
this.price = price;
}
//데이터타입에 따라 중복이 허용되지 않는다
// _01_airCon(String company, int price){
// this.company = company;
// this.price = price;
// }
_01_airCon(String company, String color, int price, int size, int temp){
this.company = company;
this.color = color;
this.price = price;
this.size = size;
this.temp = temp;
}// 기본적인 생성자를 기억하자!
// 기본생성자를 알면 매개변수 생성자에 입혀 this.(변수) = (변수); 지정 필수
// 매개변수 순서 꼭 알기!!!
(3) 메소드
[3] 메소드
/*
데이터타입 메소드이름(매개변수){
실행내용;
(데이터타입)리턴값;
}
*/
// boolean state = false; //에어컨 전원상태 여부를 나타내는 변수(on/off)
//
// boolean onPower() {
// // Add return statement : 리턴문장 추가
// // Change return type to 'void' : 리턴타입을 void로 바꿔라
//
// state = true;
// return state;
//
// }
// boolean run = onPower();
// Q. run의 값은?? true가 된다
void onPower() {
System.out.println("에어컨 전원 On!");
}
// 메소드 이름도 중복X
void offPower() {
System.out.println("에어컨 전원 Off!");
}
//온도 1 증가
void upTemp() {
temp++;
}
//온도 1 감소
void downTemp() {
temp--;
}
//현재 온도
int curTemp() {
return temp;
}
}// void 메소드명() {
// System.out.println("아무거나" + 변수);
// }
[1] main 알기!
package Java0329;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _01_airConMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Scanner객체 생성
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//클래스 Scanner 생성자Scanner
// 객체생성를 통해서 필드와 생성, 메소드 사용
// _01_airCon 객체 생성 : 기본생성자
_01_airCon aircon = new _01_airCon();
// _01_airCon 객체 생성 : 매개변수 생성자
_01_airCon aircon1 = new _01_airCon("삼성", 20);
// 객체의 멤버 변수(필드)에 접근하는 방법 : 도트(.)연산자 사용
aircon.color = "white";
aircon.price = 160;
aircon.temp = 21;
System.out.println("색상 : "+ aircon.color);
System.out.println("가격 : "+ aircon.price);
System.out.println("온도 : "+ aircon.temp);
System.out.println("회사 : "+ aircon1.company);
System.out.println("크기 : "+ aircon1.size);
aircon.color = "white";
aircon.price = 160;
aircon.temp = 21;
System.out.println();
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
aircon1.color = "white";
aircon1.price = 160;
aircon1.temp = 21;
System.out.println("색상 : "+ aircon1.color);
System.out.println("가격 : "+ aircon1.price);
System.out.println("온도 : "+ aircon1.temp);
System.out.println("회사 : "+ aircon1.company);
System.out.println("크기 : "+ aircon1.size);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("메소드 호출(실행)");
// 메소드 호출(실행)
aircon.onPower();
System.out.println("현재온도 : " +aircon.curTemp());
aircon.downTemp();
System.out.println("현재온도(1도 Down) : " +aircon.curTemp());
aircon.upTemp();
aircon.upTemp();
System.out.println("현재온도(2도 Up) : " +aircon.curTemp());
aircon.offPower();
}
}// main이라는 class를 새로 만들어서 앞전에 만들던 class를 불러와서 최종 출력을 도와준다는 개념
// 입력을 먼저 불러올 Scanner객체를 생성
// 객체생성을 통해 기본생성자를 만들고 거기에 매개변수 생성자를 만들어서 사용한다.
// 객체 멤버에 적용시키려면 도트(.) 연산자 사용해서 꼭 불러오기!
//출력

[1] main 알기! 2
package Java0329;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _01_airConMain2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 에어컨 2대 생성
// (1) 기본생성자 설계
// (2) 모든 매개변수 생성자 설계
_01_airCon aircon = new _01_airCon();
_01_airCon aircon2 = new _01_airCon("LG", 34);
aircon.color = "검정색";
aircon.price = 300;
aircon.temp = 24;
System.out.println("색상 : "+ aircon.color);
System.out.println("가격 : "+ aircon.price);
System.out.println("온도 : "+ aircon.temp);
System.out.println("회사 : "+ aircon2.company);
System.out.println("크기 : "+ aircon2.size);
System.out.println(aircon2.company+"사의 "+ aircon.color+"의 "+aircon.price+"만원짜리 "+ aircon2.size+"평형 에어컨의 온도를 " + aircon.temp+"도로 설계");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("리모콘");
aircon.onPower();
System.out.println("현재온도 : " +aircon.curTemp());
aircon2.downTemp();
System.out.println("현재온도(1도 Down) : " +aircon2.curTemp());
aircon2.upTemp();
aircon2.upTemp();
System.out.println("현재온도(2도 Up) : " +aircon2.curTemp());
aircon.offPower();
}
}//출력


[2] carClass
매개변수 작성법 중요!!!

(1) 필드
public class _02_car {
// 클래스 3요소
//[1] 필드
// 색상(color), 최고속도(speed), 연료타입(type), 모델명(model)
// 회사(company)는 "현대"로 지정
String color;
String commpany = "현대";
int speed;
String type;
String model;(2) 생성자
//[2] 생성자
//(1) 기본생성자
public _02_car(){
}
//(2) 모든 매개변수를 가지는 생성자
_02_car(String color, String commpany, int speed, String type, String model){
this.color = color;
this.commpany = commpany;
this.speed = speed;
this.type = type;
this.model = model;
// this를 사용하면 필드, 사용하지 않으면 매개변수값
}(3) 메소드
//[3] 메소드
// 자동차 정보를 출력하는 메소드
void carInfo() {
System.out.println("색상 : " + color);
System.out.println("속도 : " + speed);
System.out.println("타입 : " + type);
System.out.println("모델명 : " + model);
System.out.println("제조사 : " + commpany);
}
// 필드 추가
int gas;
// 메소드 추가 : gas 충전
void setGas(int gas) {
this.gas = gas;
}
// 주행 메소드
void drive() {
boolean run = isLeftGas();
while(run) {
if(gas >0) {
System.out.println("주행합니다. (gas잔량 : " + gas + ")");
gas--;
}else {
System.out.println("멈춥니다. ("+ gas + ")");
run=false;
}
}
}
// 연료확인 메소드
boolean isLeftGas() {
if(gas!=0) {
System.out.println("gas "+ gas + "만큼 남아있습니다." );
return true;
}else {
System.out.println("gas가 없습니다" );
return false;
}
}
}[2] main 알기!
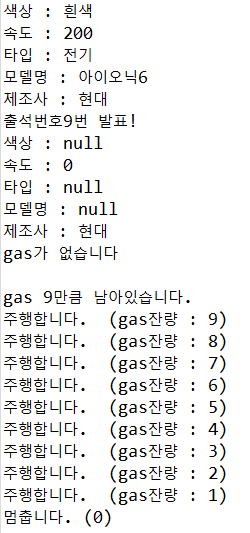
public class _02_carMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// myCar객체를 기본생성자 만들고
// 내가 원하는 자동차 정보를 입력!
_02_car myCar = new _02_car();
myCar.color = "흰색";
myCar.model = "아이오닉6";
myCar.speed = 200;
myCar.type = "전기";
myCar.carInfo();
// 조원 차량을 매개변수 생성자로 만들고
// carInfo()메소드를 사용해 출력!
_02_car hsCar = new _02_car();
// 발표자
int n = (int) (Math.random() * 14) + 1;
System.out.println("출석번호" + n + "번 발표!");
hsCar.carInfo();
hsCar.drive();
System.out.println();
hsCar.setGas(n);
hsCar.drive();
}
}//출력
[3] StudentClass
(1) 필드
// 필드
String name;
int age;
String address;
String contact;(2) 생성자
// 기본생성자!!
Student() {
}
// 매개변수 생성자
Student(String name, int age, String address, String contact) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
this.contact = contact;
}(3) 메소드
// 메소드
void StuInfo() {
System.out.println("이름 : " + name);
System.out.println("나이 : " + age);
System.out.println("주소 : " + address);
System.out.println("연락처 : " + contact);
}
}[3] main 알기!
// 입력받기 위한 빈 배열로 만들고
// 입력 받기 위한 변수를 지정!
// 입력받은 변수에 각 메소드 지정!
// 변경할 조원만큼 메소드을 불러와 변경될 변수를 추가 지정해 줘서 조건문으로 선택한다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StudentMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 입력받기 위한 Scanner
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Student란 변수에 빈 배열로 함
Student[] student = null;
// 학생 값을 받을 변수
int stuNum = 0;
boolean run = true;
int menu;
while (run) {
System.out.println("=================================================");
System.out.println("1.학생수 | 2.정보입력 | 3.정보출력 | 4.정보수정 | 5.종료");
System.out.println("=================================================");
System.out.print("선택 : ");
menu = sc.nextInt();
switch (menu) {
case 1: // 입력받을 학생수
System.out.println("학생 수 : ");
stuNum = sc.nextInt();
break;
case 2: // 학생수 받은만큼 이름, 나이, 주소, 연락처출력
student = new Student[stuNum];
for (int i = 0; i < student.length; i++) {
Student stu = new Student();
System.out.println((i + 1) + "번 학생 정보 입력");
System.out.println("이름 입력 : ");
stu.name = sc.next();
System.out.println("나이 입력 : ");
stu.age = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine().trim();
System.out.println("주소 입력 : ");
stu.address = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("연락처 입력 : ");
stu.contact = sc.next();
System.out.println();
student[i] = stu;
}
break;
case 3: // 조원의 stuInfo를 불러와 보여준다
for (int i = 0; i < student.length; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + "번 조원입력");
student[i].StuInfo();
System.out.println();
}
break;
case 4: // 변경될 수 만큼 변경 선언해주기
System.out.println("변경할 학생의 이름 입력 : ");
String cName = sc.next();
int check = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < student.length; i++) {
if (cName.equals(student[i].name)) {
System.out.println("변경할 나이 : ");
student[i].age = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine().trim();
System.out.println("변경할 주소 : ");
student[i].address = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("변경할 연락처 : ");
student[i].contact = sc.next();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("변경된 정보");
student[i].StuInfo();
check++;
}
if(check == 0) {
System.out.println("없습니다");
}
}
break;
case 5: // 종료
run = false;
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
break;
default:
System.out.println("다시 입력하세요");
break;
}
}
}
}//출력

